A Non-vibratory, Low Noise Method that Can Be Used Close to Existing Structures
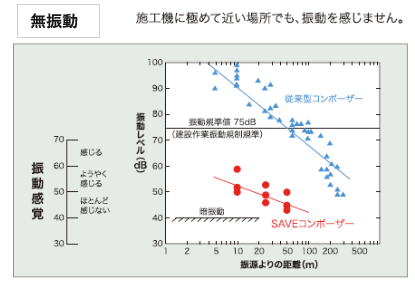
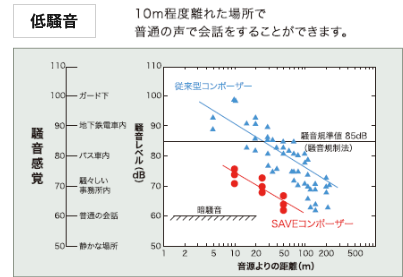
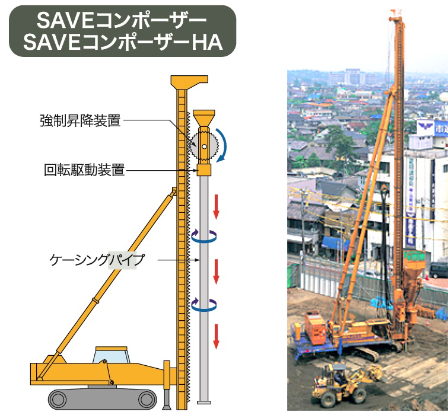
The SAVE Compozer uses a forced driving/lifting device that rotates a casing pipe to penetrate the ground. After the casing pipe reaches a certain depth, repeated lifting and driving in a wave-like pattern as the sand is discharged compacts the sand into a large-diameter, well compacted pile. With no use of vibration energy, compaction does not create loud noise.
| New civil engineering technology | May 1999: Japanese Geotechnical Society, 1998 Technology Development Award July 1999: Japan Architectural Center, Concrete Structure Evaluation Committee, Evaluation no. BCJ-C2273 September 1999: Ministry of Transport, Technical Appraisal no. 99107 April 2000: Science and Technology Agency, short-listed for 59th Noted Innovation Award April 2010: Selected as recommended technology, Ministry of Land, Infrastructure, Transport and Tourism June 2017: Japan Institute of Country-ology and Engineering, General Civil Engineering Methods Technical Study Certificate no. 42 |
|---|
Features
- This non-vibratory, low noise method causes minimal impact on the surrounding environment and so can be implemented close to existing structures.
- It can be used for the same improvement objectives as conventional sand compaction pile methods, and gives the same improvement effect.
- CONOS is a new system used for implementation management. The CONOS system provides the operator with specific instructions and is a trustworthy system for creating sand piles with precision.
- This method can be used for all types of ground, from sandy to clay.
- Besides sand, other types of material such as crushed stone/concrete or slag can be used as the pile material. The pile diameter can easily be changed using the same installation rig, so composite piles with sand drains can be installed. Implementation cost is economical compared with other types of environment-friendly ground improvement methods.
- By using an ejector discharging device that mixes in compressed air and water, it’s possible to use in sand layers with N values around 35 included within soft ground that conventionally require prior boring with an earth auger or similar. (SAVE-HA)
- A message displayed on the monitor screen indicates that the bearing layer has been reached, for highly reliable implementation management. (SAVE-HA)